Describe How Opportunity Cost Is Used in Decision Making
Opportunity Cost Decision Making. Explain with the help of a numerical example.

Optimal Decision Making And Opportunity Costs Video Khan Academy
2 broader benefits should be assessed as well as the monetary benefits.
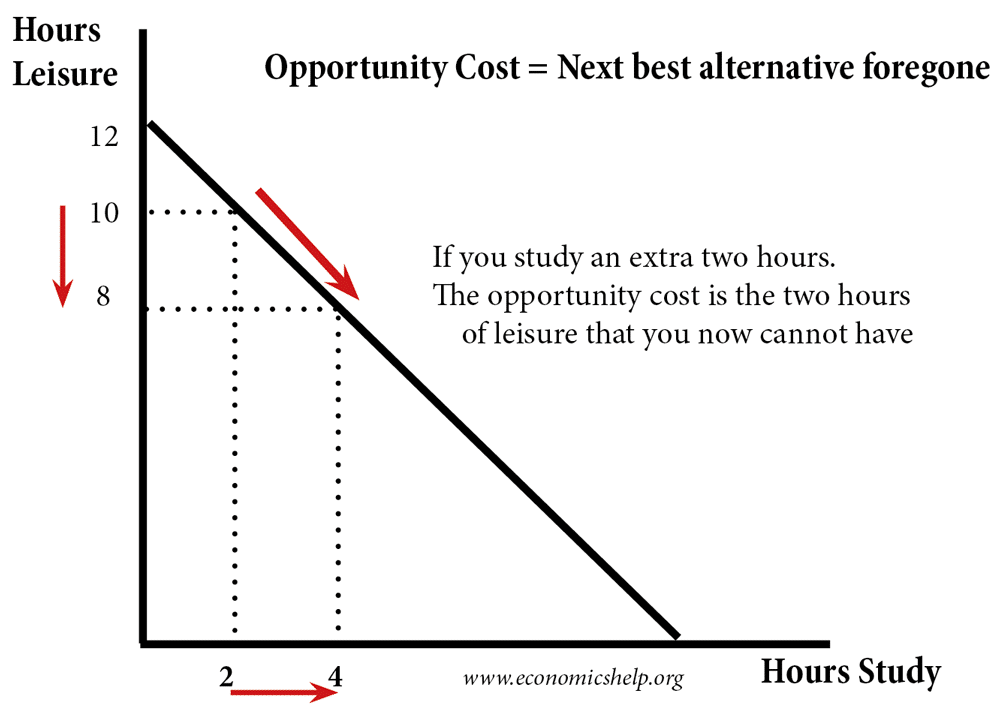
. Virtually every alternative has some opportunity cost attached to it. Forgo my prime working years earning potential and slow our net worth velocity. Businesses make a variety of decisions on a daily basis and each of these decisions implies an opportunity cost.
This cost is not only financial but also in time effort and utility. The amount of other products that must be sacrificed to obtain more of any given product is called the opportunity cost. The term joint cost is used to describe the costs incurred after the split-off point in a process involving joint products.
When assessing Opportunity Cost its important to keep these three things in mind. The benefit or value that was given up can refer to decisions in your personal life in a company in the economy in the environment or on a governmental level. Opportunity cost is the comparison of one economic choice to the next best choice.
What is opportunity cost. Opportunity Costs Capital Budgeting Methods Opportunity Costs In Your Decision Making. A common formula for finding opportunity cost is.
The more of a product produced the greater is its marginal opportunity cost. Opportunity Cost of Choice 1. The slope of the.
However if companys return is only 3 when we could have made a return of 9 from FD then our opportunity cost is 9 3 6. In a decision analysis situation which one of the following costs is not like to contain a variable cost component a. Costs may be classified as differential cost opportunity cost and sunk cost.
It is not only individuals and households that face opportunity cost but businesses and governments as well. Louis Fed in a recent Page One Economics. Opportunity cost Return on the option not chosen - Return on chosen option.
The company decides to consider opportunity cost as it help in decision making process. If you decide to purchase a new piece of equipment your opportunity cost is the money spent elsewhere. For example Bill Gates dropped.
Relevant Cost and Irrelevant Cost. Miss out on my childrens prime years of development. Money and Missed Opportunities.
Opportunity costs are a. The forgone salary would be an opportunity cost of seeking further education. Opportunity cost for business and government.
2009 describes opportunity cost of engaging in an activity is the cost of the next most desirable alternative activity that a person have to give up in order to engage in that activity. How Opportunity Cost Can Help You Make Better Decisions with Examples How to determine opportunity cost. Since resources are limited every time you make a choice about how to use them you are also choosing to forego other options.
In the beginning I closely considered Choice 1. Opportunity costs are relevant in business decision makingIn addition companies commonly use them when. Avoidable Cost and Unavoidable Cost 9.
The cost concepts are. Opportunity costs is not usually entered in the accounting records of an organisation but it is a cost that must be explicitly considered in every decision a manager makes. Opportunity costs are measured in terms of real goods rather than money market prices are not part of the production possibilities model 3.
These comparisons often arise in finance and economics when trying to decide between investment options. I thought earning more money would eventually lead to more freedom and choice later on with my family. Opportunity Cost of Choice 2.
Example of Opportunity Costs in Decision-Making. Opportunity cost is the value of the next-best alternative when a decision is made. Not used for decision making.
Differential cost also known as. Opportunity cost is the cost of taking one decision over another. Such costs do not require cash outlays and are only imputed costs.
Using this formula and the below steps you can calculate opportunity cost. A decision-making concept described as the contribution to income that is foregone by not using a limited source for its best alternative use is called a. In business opportunity costs play a major role in decision-making.
And 3 each option needs to be assessed based on the same criteria ie. The work of managers includes comparison of costs and revenues of different alternatives. Opportunity cost if the foregone cost it is cost which is chosen by leaving the next best alternative.
1 to make an informed economic decision the value of an opportunity needs to be assessed based on both the benefits and the costs associated. Opportunity cost can lead to optimal decision making when factors such as price time effort and utility are considered. 10032015 0138 PM Tutorial.
700 560 Posted By. The opportunity cost attempts to quantify the impact of choosing one investment over another. If a business for instance decides to use its personnel to upgrade its customer database.
It helps the producer to decide whether to go for the prod. Economists use the term opportunity cost to indicate what must be given up to obtain something thats desired. Cost Concept 1.
A fundamental principle of economics is that every choice has an opportunity cost. Opportunity cost is not usually entered in the accounting records of an organization but it is a cost that must be explicitly considered in every decision a manager makes. An opportunity cost is a hypothetical cost incurred by selecting one alternative over the next best available alternative.
Describe how opportunity cost is used in decision making Available for. Its necessary to consider two or more potential options and the benefits of each. The following points highlight the top nine cost concepts used in decision making.
Its what is given up explains Andrea Caceres-Santamaria senior economic education specialist at the St. A cost that is traceable to a segment through activity-based costing may or may not be an avoidable cost for decision making. Simply put the opportunity cost is what you must forgo in order to get something.
An opportunity cost is the cost of an alternative that must be forgone in order to pursue a certain action. Decision-making is selecting the best alternative which is facilitated by the help of opportunity costs. Opportunity cost is the potential loss from a missed opportunitythe result of choosing one alternative and forgoing another.
This classification is made for decision making purposes. Out of Pocket Costs 3. Opportunity cost is a simple and one of the most significant concepts of microeconomics Frank.
Man typing while copying a book as opportunity cost examples. Companies must take both explicit and implicit costs into account when making rational business decisions. Explanation and examples of differential opportunity and sunk costs are given below.
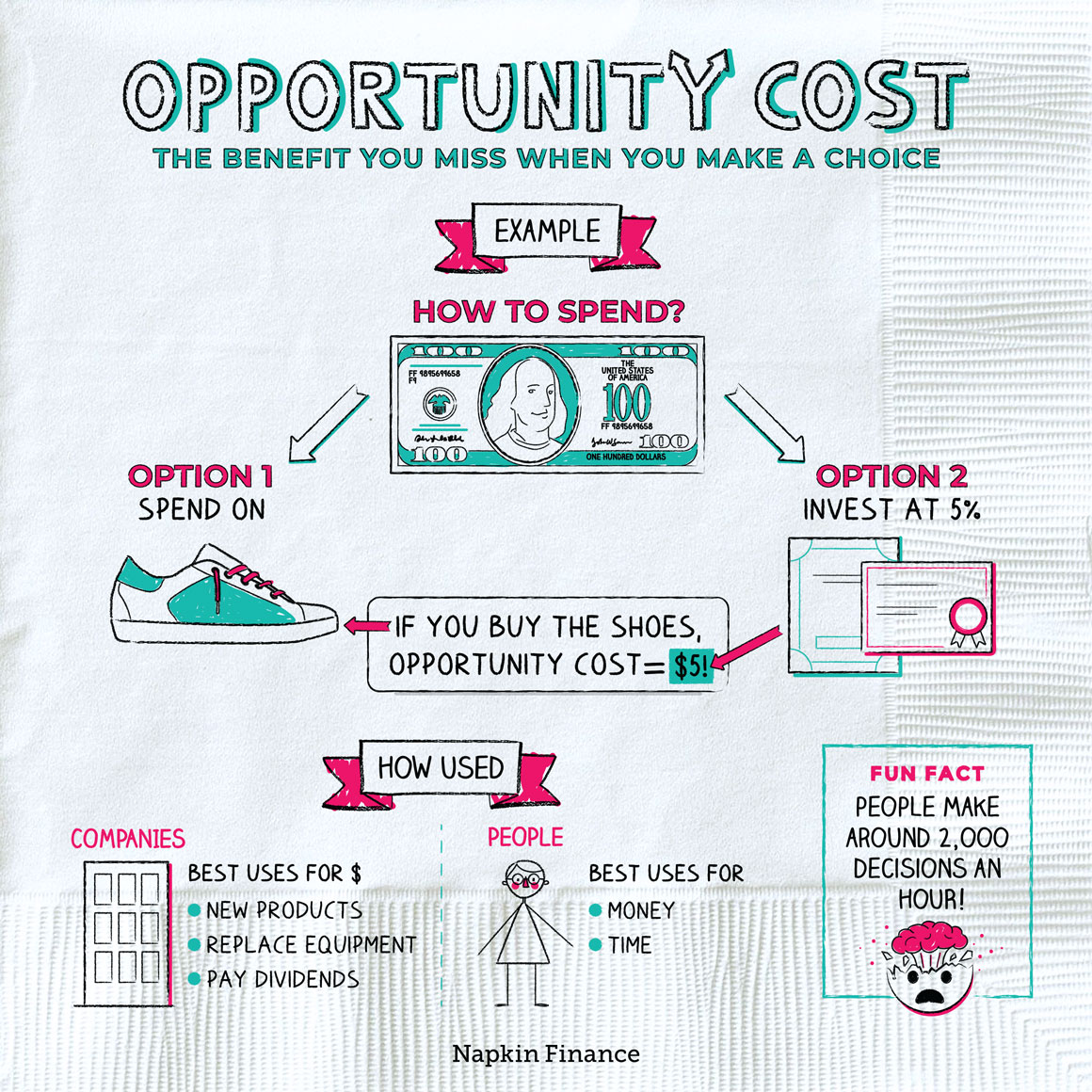
What Is Opportunity Cost Investment Opportunities Napkin Finance

No comments for "Describe How Opportunity Cost Is Used in Decision Making"
Post a Comment